Supraspinatus Muscle Pain
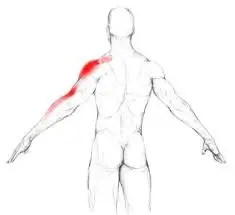
Supraspinatus Muscle Pain occurs due to strain, overuse, or injury to the supraspinatus muscle, a key component of the rotator cuff in the shoulder. Pain is often felt on the top or side of the shoulder and may worsen with overhead movements.
Common causes include repetitive stress, poor posture, or rotator cuff injuries. Early management with rest, stretching, strengthening, and proper biomechanics can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
What is a Supraspinatus Muscle Pain?
The supraspinatus muscle in the shoulder plays a crucial role in arm movement and stability. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles responsible for lifting the arm and supporting the shoulder joint. Supraspinatus muscle pain is a common issue that can arise due to overuse, injury, or degenerative conditions. This type of pain can significantly affect daily activities, causing pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for supraspinatus muscle pain is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
One essential component of the shoulder’s rotator cuff is the supraspinatus muscle. It stabilizes the shoulder joint and aids in arm abduction, which is the raising of the arm away from the body. Pain, weakness, and limited shoulder movement are prominent symptoms of supraspinatus muscle pain, which can be caused by overuse, injury, or degenerative changes.
Anatomy of the Supraspinatus Muscle
Together with the teres minor, subscapularis, and infraspinatus, the supraspinatus muscle is one of the shoulder’s four rotator cuff muscles. It is essential for supporting shoulder movements and stabilizing the glenohumeral joint.
Location and Structure
- The supraspinous fossa of the scapula, or shoulder blade, is where the supraspinatus muscle begins.
- It travels through a small opening known as the subacromial space beneath the scapula’s acromion.
- It attaches to the humerus’s (upper arm bone) greater tubercle.
- The supraspinatus tendon, which covers the muscle, is vulnerable to damage and deterioration.
Function of the Supraspinatus Muscle
- Arm Abduction: The deltoid muscle takes over after the supraspinatus performs the first 15 degrees of arm raising.
- Shoulder Stability: It prevents dislocations by keeping the humeral head in the glenoid cavity.
Causes of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain:
Overuse, trauma, and degenerative changes are some of the causes of pain in the supraspinatus muscles. The most frequent causes are listed below:
Injuries from Overuse and Repetitive Motion
- Throwing, swimming, and lifting weights are examples of repetitive overhead exercises that can cause strain on the supraspinatus muscle.
- prevalent in manual laborers (painters, construction workers) and athletes (tennis players, baseball pitchers).
- causes weakening, irritation, and micro tears over time.
Supraspinatus Tendinitis
- inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon caused by incorrect mechanics or excessive use.
- Tenderness, stiffness, and pain when moving the arms are some of the symptoms.
Tears in the Rotator Cuff
- rips in the supraspinatus tendon, either partial or total.
- can be caused by gradual degeneration or abrupt trauma (such as falls or carrying large objects).
- causes weakening, restricted motion, and excruciating shoulder pain.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
- Between the acromion and the humeral head, the supraspinatus tendon is squeezed.
- causes pain, swelling, and limited mobility, particularly when moving upwards.
- Muscle imbalances or bad posture may make it worse.
Unbalanced muscles and bad posture
- Extra strain is placed on the supraspinatus by forward head posture and round shoulders.
- Improper mechanics may be caused by weakness in the scapular stabilizers, such as the trapezius and serratus anterior.
Aging and Degenerative Changes
- The tendon gets less elastic with time and is more vulnerable to damage.
- common in those over 40, resulting in deterioration of the rotator cuff.
Direct Injury and Trauma
- Damage to the supraspinatus may result from falls onto an outstretched arm or dislocation of the shoulder.
- Tendon tears or inflammation may be the outcome of sudden impact injuries.
Nerve compression (entrapment of the suprascapular nerve)
- The supraspinatus muscle may become weak and painful if the suprascapular nerve is compressed.
- may be caused by cysts, bone spurs, or recurrent shoulder strain.
Symptoms of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain:
Depending on how severe the injury or ailment is, several symptoms can accompany supraspinatus muscle pain. Typical signs and symptoms include:
- Pain in the Shoulders
- Pain in the upper and outer regions of the shoulder that is dull or painful.
- Although it typically doesn’t go past the elbow, pain can travel down the upper arm.
- Activities that involve lifting, reaching, and throwing are worse.
- Weakness in the Arm and Shoulder
- Lifting or holding objects away from the body can be challenging.
- diminished strength when moving above the ground.
- may have trouble doing everyday tasks like getting dressed, combing their hair, or carrying a bag.
- Restricted Motion
- Raising the arm above shoulder level is difficult.
- shoulder stiffness and soreness, particularly after rest.
- Pain between 60° and 120° of arm abduction is known as the painful arc sign.
- The sensation of clicking or popping
- popping, clicking, or grinding noise as the shoulder is moved.
- maybe a sign of bursitis, tendon injury, or impingement.
- Pain at Night and Uncomfortable Sleep
- increase pain while the affected shoulder is lying down.
- gets worse at night, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Tenderness and Swelling
- soreness or swelling in the vicinity of the shoulder joint.
- The supraspinatus tendon may be sensitive to pressure or contact.
Treatment of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain
The severity of the condition determines the course of treatment for supraspinatus muscle pain, which can range from conservative measures to surgery in extreme situations. Reducing pain, regaining shoulder function, and avoiding more injuries are the objectives.
You might use home remedies to reduce pain and promote recovery in addition to shoulder workouts.
Compress, ice, and rest your shoulder with the RICE technique. Raise your shoulder above your heart whenever you can. Additionally, you can take an Epsom salt bath or apply a heating pad.
You can use over-the-counter painkillers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce pain. Or try using natural remedies like cloves, willow bark, or turmeric to ease pain. Several times a day, use an essential oil combination, menthol rub, or arnica cream on the affected area.
Frequent acupuncture and massage therapies might help your body regain equilibrium and ease pain. Additionally, you can experiment with manipulative therapies like rolfing, osteopathic adjustments, and chiropractic adjustments.
- Modification of Rest and Activity
keep away of hard lifting and repetitive overhead motions.
Adjust your activities to lessen shoulder strain. - Heat and Ice Therapy
Ice packs (15–20 minutes, three times a day) help to relieve pain and inflammation.
Heat therapy promotes blood flow and eases tense muscles. - Medicines Pain relievers (like acetaminophen) for mild to moderate pain and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (like ibuprofen and naproxen) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Injections of Corticosteroids
used to treat chronic pain and inflammation.
injected to lessen edema in the subacromial space.
should be applied with caution because the tendon may get weaker with repeated injections.
Physical Therapy Treatment of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain:
Across-the-chest stretch

- Cross your right arm over your chest.
- Hold this position for no more than a minute.
- On the other side, repeat.
- Repeat 3–5 times on each side.
Neck release
- Your shoulders and neck might become less tense with this moderate exercise.
- Put your chin down close to your chest. Your neck will be strained near the nape.
- Keep your posture for no more than a minute.
- On the other side, repeat.
- Repeat 3–5 times on each side.
To make this stretch deeper:
- Keep your chin pressed on your chest.
- Attempt to hold this position for no more than one minute.
- On the other side, repeat.
- Repeat 3–5 times on each side.
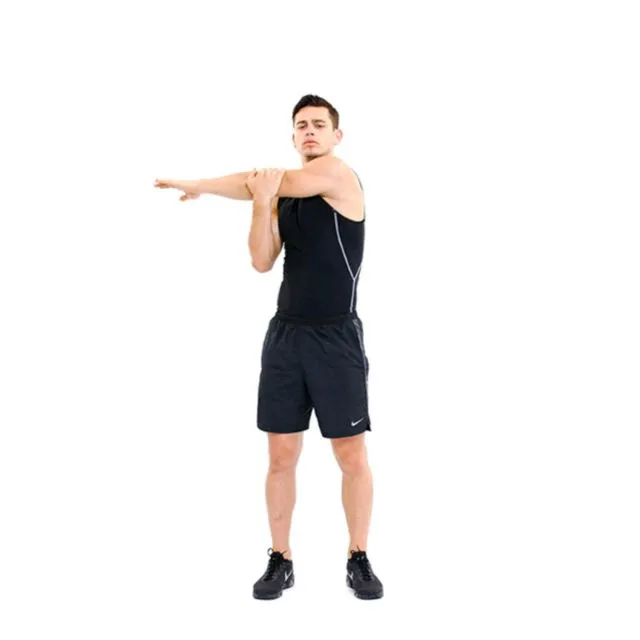
Chest expansion

- Spread your shoulder blades out over your chest and move them nearer each other.
- Look up at the ceiling with your chin up.
- Hold for a maximum of thirty seconds.
- Do this three to five times.
Eagle arms spinal rolls
- If you have trouble with the arm position, you can do this exercise by holding the opposing shoulders.
- Sitting, extend your arms to the sides.
- For fifteen seconds, maintain this posture.
- As you exhale, pull your elbows in toward your chest and roll your spine.
- For one minute, keep doing this motion.
- On the other side, repeat.
Seated twist
- Your hips should remain facing forward during this exercise.
- Your right hand should be placed wherever it feels most comfortable.
- On the left side, repeat.
- Repeat 3–5 times on each side.
Shoulder circles
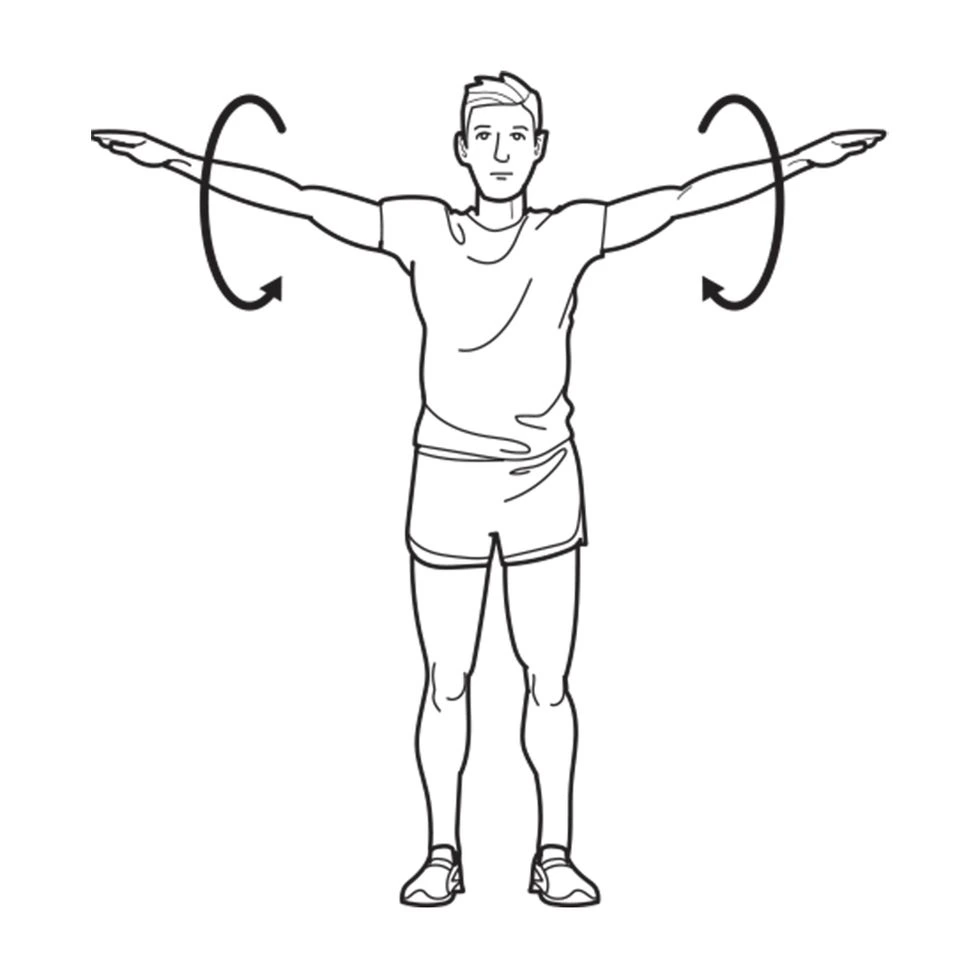
- Let your right-hand dangle downward.
- Do the same on the opposite side.
Doorway shoulder stretch
- Bend forward while using your core.
- Stretch again with your left foot forward.
- Do each side two or three times.
Downward Dog Pose
- Get on your hands and knees to begin.
- Bring your head toward your feet so that your shoulders are flexed overhead while maintaining a straight spine.
Child’s Pose

- Your neck, shoulders, and back will all feel less tense after doing this calming pose.
- Let your shoulders and spine relax as your chest drops heavily toward the floor.
Thread the needle
- Your shoulders, upper back, and chest will all feel less tight after doing this pose.
- Lift your right hand toward the heavens with the palm pointing away from your body.
- Lower your arm until it reaches to your left side and is beneath your chest, palm up.
- To prevent collapsing into this space, engage your right arm and shoulder.
- Before doing this stretch again on the left side, unwind in Child’s Pose.
Prevention of Supraspinatus Muscle Pain:
- To prevent shoulder impingement, keep your posture straight.
- To increase stability, strengthen your rotator cuff muscles.
- Stretching and good ergonomics can help prevent repetitive strain.
- Before lifting weights or doing sports, warm up.
FAQs
What is the supraspinatus muscle orthopedic test?
Test for Supraspinatus
We can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then bring them anteriorly with a 30° forward flexion to check the integrity of the supraspinatus. The patient will be asked to push both arms upward against our resistance while in this position.
When the supraspinatus is stretched, how long does healing take?
If you work a desk job, it can take four weeks to get back to work. You will have to wait at least three months if you have to lift at work. Following rotator cuff surgery, you will require rehabilitation. This usually lasts 4 to 9 months and begins about 2 weeks following surgery.
Can a massage help with a supraspinal tear?
There are numerous muscle adhesions in your teres minor, subscapularis, infraspinatus, and supraspinatus. For the elimination of knots, particularly in the subscapularis, a combination of trigger point therapy and deep tissue massage can be highly beneficial.
What makes the supraspinatus weak?
People over 40 are more susceptible to degeneration and rotator cuff tears because of the body’s natural weakening of the soft tissue over time, which is commonly caused by misuse of the supraspinatus tendon.
How can I determine whether my supraspinatus is tight?
Localized pain and sensitivity on the front side of the shoulder are the primary symptoms of supraspinatus tendinosis. When you raise your arm, you may experience pain and stiffness. When lowering your arm from the elevated posture, you may also experience pain. Symptoms may be modest at first.
Which medications are effective for supraspinatus?
Summary of Medication
A brief course of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) is appropriate as an adjuvant to the therapy program and other treatment modalities during the acute to subacute phases of shoulder impingement syndrome due to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Is the muscle of the supraspinatus deep?
The rotator cuff muscles include the subscapularis, teres minor, infraspinatus, and supraspinatus. Stretching from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula to the proximal humerus, the supraspinatus is situated deep in the trapezius muscle in the posterior scapular area.
For supraspinatus pain, which massage is most effective?
One of the most effective treatments for shoulder and back aches and pains is sports massage, a firm, focused type of therapy that targets the soft tissues. Both professional and amateur athletes, as well as those who do not routinely exercise, can find it to be quite beneficial.
What is supraspinatus physical therapy?
Physical Therapy
Supraspinatus, internal and external rotators, prone extension, horizontal abduction, forward flexion to 90°, upright abduction to 90°, shoulder shrugs, rows, push-ups, press-ups, and pull-downs are examples of isotonic resistance exercises that are used to strengthen the scapular stabilizers.
How should I sleep if I have pain in my supraspinatus?
Dozing Off on Your Back
By raising the shoulder’s ball and socket joint, relieves pressure on the muscles, ligaments, bursae, and joint structures while also offering appropriate anatomical support. According to recent research, adopting this sleeping position can help reduce shoulder pain and encourage deeper, more restful sleep.
What is the duration of supraspinatus pain?
Over time, the majority of shoulder tendonitis instances resolve on their own. Depending on how severe it is, recovery could take weeks or months. Consult your physician if you: Feel pain that makes it difficult for you to carry out your daily tasks.
How is supraspinatus released?
Raise the arm to slightly above 90 degrees of shoulder abduction to start the active release. Pull the shoulder into adduction behind your back with your other hand after lowering the arm to a neutral posture. Repeat up to two or three different locations and up to six repetitions.
Can the supraspinatus muscle be massaged?
Self-massage is known as supraspinatus. I suggest using the Trigger Fairy to massage this muscle. This is the simplest and most secure method of applying pressure. Although it is a little more challenging and inconvenient, using a massage ball is still feasible and beneficial.
How is a supraspinatus strain treated?
Physical therapy, rest, cold packs, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are all part of this treatment. Physical treatment can also be supplemented with corticoid injections. If, after three to six months of conservative treatment, there is no improvement, surgery may be the answer.
What signs of pain in the supraspinatus are present?
A feeling of burning in the shoulder. weakness when pushing a door open or lifting something heavy. Sleep was disturbed by the ache. difficulty carrying out daily tasks like putting on a jacket or brushing one’s hair.
References
- ProHealth Prolotherapy Clinic. (2025, January 25). Supraspinatus tendonitis – causes & best treatment options in 2025. https://prohealthclinic.co.uk/blog/supraspinatus-tendonitis/
- Faoa, T. M. D. M. F. (n.d.). Supraspinatus tendonitis: Practice Essentials, etiology, Epidemiology. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/93095-overview