Passive Range Of Motion (PROM) Exercises
What is a Passive Range Of Motion Exercise?
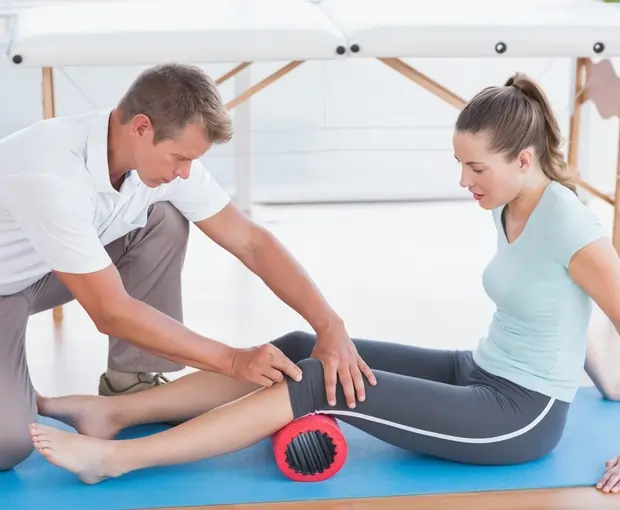
Exercises for passive range of motion (PROM) are an essential part of physical therapy and rehabilitation regimens. In these exercises, a therapist or external force gently moves a joint through its whole range of motion without the patient’s active involvement. When a patient is unable to move a joint on their own because of an injury, surgery, pain, or other medical condition, PROM exercises are usually recommended.
Maintaining or enhancing joint flexibility, preventing the onset of contractures (shortening of muscles and tendons), and promoting circulation in the affected area are the main objectives of PROM exercises. People healing from orthopedic procedures, such as joint replacements, or those suffering from illnesses like arthritis, stroke, or paralysis, will find these exercises very helpful.
What is Range Of Motion (ROM)?
A joint’s range of motion is evaluated during two distinct actions. Either passive ROM (PROM) or active ROM (AROM) on its own.
A physical therapy assessment or plan of action usually includes an evaluation of the range of motion. In varied degrees, depending on the individual and the physical component, these are deemed normal. Increased range of motion is the aim of training while limiting the development of ligament, tendon, and capsule shortening, as well as contractures and adaptive muscle shortening. ROM exercises also excite the senses.
Type of Range Of Motion(ROM)
- Passive Range Of Motion
- The term “passive range of motion” (PROM) refers to the maximum range of motion that a joint can typically achieve when it is moved solely by an external force, such as a therapist or a CPM machine.
- Active-assisted Range Of Motion
- mostly used when a patient’s muscles are weak, worn out, or toned differently and thus require assistance with an outside power to move them.
- Active range of motion:
- The range of motion that is possible when opposing muscles contract and relax to cause joint movement is known as the active range of motion (AROM). For example, the triceps must relax and the biceps must tighten to allow the elbow to flex. The active range of motion is frequently limited, in contrast to the passive range of motion. when the patient is able to control, coordinate, and contract their movement consciously; they often do this on their own.
What is Passive ROM exercise?
In the context of fitness and rehabilitation, the words “passive range of motion” and “active range of motion” are frequently employed. While increasing a joint’s range of motion is the common objective, there are differences across the methods.
A passive range of motion is when a physical therapist or other caregiver physically moves or stretches a body part, such as your hand or leg. If you find joint exercises difficult or impossible to perform at all, a family member or physical therapist is available to help.
Put another way, you can get help from someone else if you are unable to actively engage in range-of-motion activities.
In the field of rehabilitation, this is something that is becoming more common. An individual’s range of motion can be increased by a machine or a physical therapist (particularly when it comes to the joints and ligaments).
Measuring the range of motion(ROM)
Goniometer: The profession of physical therapy is essentially centered on tracking patients’ health and progress. ROM measurements are a vital part of the evaluation process for physical therapy.
One common tool for determining the range of motion of a bodily joint is a goniometer. It computes joint angles from the joint axis using a stationary arm, fulcrum, and moving arm. Accurate results when measuring ROM with a goniometer require training. For information on how to position the goniometer precisely and consistently to find the range of motion, see the goniometry collection of pages.
One more method to quantify the range of motion (ROM) is to use tape measures to assess the degree of flexibility of different body components. For example, the Schober Test makes it possible to measure lumbar spine flexion with a tape measure.
Uses Of Passive Range Of Motion Exercises?
You already know how easily your range of motion can be harmed if you’re coping with the aftermath of an accident to your neck, shoulders, knees, hips, or any other portion of your body.
This is due to the possibility that a joint’s range of motion the length and direction it may move in following an injury to the area may be restricted. The amount of distance and direction a joint may move, or its range of motion, is typically restricted following an injury to the affected area.
A physician, physical therapist, sports trainer, or other certified health professional can assess the degree of mobility in a joint or other body component to find out if there is a limited range of motion and to gain further insight into the effects on a specific joint. This is often carried out as part of a rehabilitation program or during a physical examination following an injury.
Passive range-of-motion exercises help you enhance your athletic performance and mobility during a training session. Exercises for passive range-of-motion must be incorporated into a passive stretching regimen. This is frequently done in group rehabilitation sessions, exercise regimens, and team sports.
Benefits of passive ROM exercises:
- Improved flow of blood
- Improved joint flexibility
- Stopping the loss of muscular mass
- Increased range of motion flexibility
- Decrease of pain
In order to improve joint mobility and prevent muscle atrophy, passive range of motion exercises can be a safe and effective treatment for those with limited mobility or who are recovering from an injury or surgery.
Disadvantages of passive ROM exercises
- limited growth of muscles
- little benefit for the heart
- Risk of injury
- Very little practical benefit
- lengthy
Risk for performing passive ROM exercise?
- People with very movable joints
- People who suffer from osteoporosis
- Individuals with inflamed joints
- People who recently underwent joint surgery
- People with severe injuries
Passive Range Of Motion Exercises in Examples:
Doorway chest stretch for the shoulders: Your shoulders will move your arms while you complete this exercise passively. The chest in the doorway extends to the shoulders. Put your elbow on the threshold of a doorway or hallway entry at a ninety-degree angle. Lean forward from the torso to open up and widen your chest.
- Exercises for the fingers and hands: Hand and finger exercises Take hold of the person’s hand with both of your hands. He or she ought to reach out and shake your hand.
- Finger bends: Pinch your fingers together to form a fist. You should move the fingers. One by one, straighten and bend each finger. Tighten and extend your thumb.
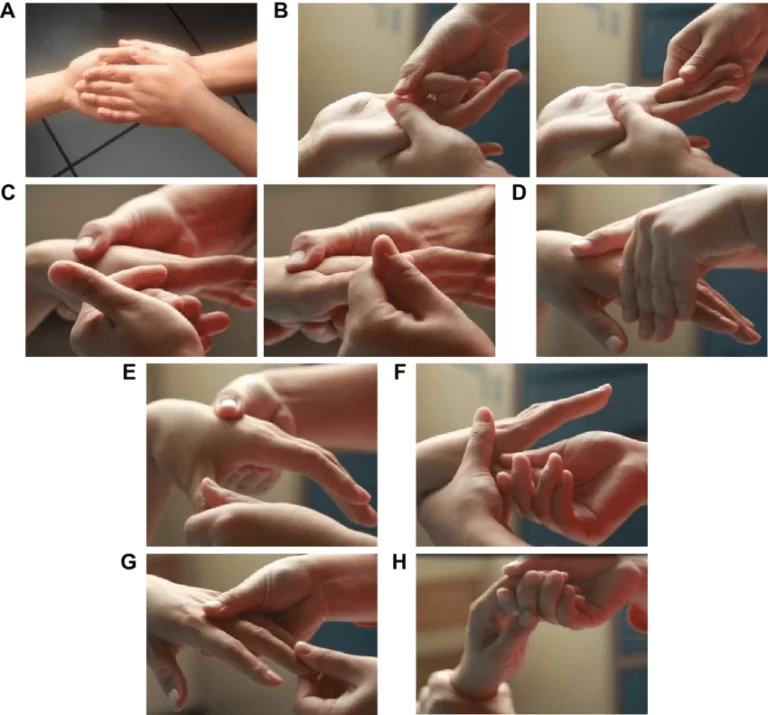
- Exercises for the knees and hips: To begin an exercise, keep your legs straight. your hand over the person’s knee. With the other hand, grasp the ankle. As you gently bend the person’s knee towards their chest, bend their hip as well. Stretch your leg slowly.
- Swaying of the legs, side to side: You can cross the leg over the other leg by returning it to the middle.
- Extension of the piriformis muscle: There is piriformis stretching, The pelvic muscle known as the piriformis, which is stretched during this exercise, forms the pigeon stance.

- For passive stretching: Lying down on the ground or at a treatment table is how you practice passive stretching. With your therapist’s help, move your leg through its passive range of motion to create resistance apart from your own weight.
- Activities for the ankles and feet: To perform foot and ankle exercises, place a wrapped towel beneath the person’s leg. Hold the person’s ankle with one hand and their toes with the other as they perform the ankle exercises. During the toe exercises, allow the participant to rest their foot on the bed while holding only their toes.
- Ankle bends: The foot points its toes upward when it is flexed at the ankle. After that, turn the foot so that the toes face the opposite direction. Rotate your ankle by lifting your foot off the mattress. It is clear that the foot is rolling. Next, shift the foot’s direction of motion.
- Side-to-side ankle movement: Turn the ankle inward such that the sole of the foot faces the leg across from it. To make the sole of the foot facing away from the opposing leg, tilt the person’s ankle outward.
Summary:
After an accident, passive range-of-motion exercises assist in maintaining your joints’ flexibility and lessen the chance that your total range of motion may be permanently reduced. This guarantees that you have enough energy to complete your everyday tasks and pursue your hobbies in addition to hastening the healing process.
FAQs
Why does the passive range of motion occur?
A joint’s maximum range of motion is typically known as passive range of motion (PROM), which is the ROM attained when an external force like a therapist or a CPM machine exclusively forces the joint to move. usually carried out when a patient is not allowed to move a body part or is unable to do so.
Is exercising by walking passively?
Your daily routine is represented by the steps you take as you walk (passive) in it. Walking from your office to the parking garage is one instance of this. This kind of passive movement is added to your daily totals by your device, but it won’t appear as a separate exercise.
What is a knee passive range of motion exercise?
Stretches and Passive Range of Motion (ROM)
Patella glide: Passive Range of Motion (PROM). superior cap (headward). Repeat inferiorly (toward the toes), laterally (outward), and medially (inward) in all directions.
What rules apply to the passive range of motion?
Guidelines for passive range of motion:
Support the joint you are moving from both above and below. Continue to move smoothly and slowly. If the joint or muscle is stiff, DO NOT FORCE the movement; instead, move the joint or muscle as far as it will allow.
What is the passive movement principle?
When someone else or specialized equipment moves a patient on their behalf, it’s known as passive movement. It is carried out with no active cooperation and total muscle relaxation.
Is passive exercise effective?
Is It Good to Exercise Passively? Passive exercise may not be as effective in helping someone lose excess weight, even though it can improve mobility, flexibility, and range of motion as well as promote muscle growth and avoid muscular weakening.
What is the passive range of motion multiplicity?
You can give your patient passive ROM exercises when she is unable to execute them actively. Move each joint through its range of motion three times, or at least twice a day, unless instructed otherwise.
How is the passive range of motion measured?
The patient is in the supine laying position in order to do a passive range of motion examination for flexion.
A passive range of motion test: why do it?
Range of motion evaluations assist us in determining whether the connective tissues around the joint, such as the ligaments, tendons, and joint capsule, have any limits. As a result, it is essential to the patient assessment process.
How can the passive range of motion be enhanced?
Exercises for the elbows and shoulders:
Raise the person’s arm forward and then up over their head to demonstrate an upward and downward shoulder movement. Return the arm to the subject’s side. Move the person’s shoulder from side to side by lifting their arm as far as possible. Return the arm to the subject’s side.
By whom is the passive range of motion performed?
In this case, joint exercises can be helped by a caregiver or physical therapist if you find them difficult or impossible to perform.
What advantages does passive range of motion offer?
For people who are unable to exercise on their own, passive range of motion activities have several advantages.
Strength of Muscles. Exercises using a passive range of motion assist in avoiding stiffness or weak muscles causes by inactivity.
Improve Circulation, Preserve Flexibility, and Lessen Pain.
What are the passive ROM tenets?
Technical Instructions
Use the appropriate hand grips or holds that the therapist has demonstrated. Within the available pain-free range of motion, perform the exercise slowly, smoothly, rhythmically, and without applying any force to the range. Perform each ROM movement with grace and softness. Never overstretch, jerk, or use force on a muscle.
Which three categories of passive movements are there?
There are three categories of passive movement: forceful passive movement, continuous passive movement, and relaxed passive movement. Passive movement is defined as moving a joint without using an active muscular contraction (CPM).
For what purpose do we use a passive range of motion?
Exercises that maintain a passive range of motion help to maintain joint flexibility. The extent to which a person’s joints can move in various directions is known as their range of motion. The exercises enable the user to fully extend every joint in their body.
What forms the basis of passive exercise?
Forced passive motions are short, localized movements in which the joints are passively moved beyond their natural range, in accordance with the passive range of motion (ROM) principle.
These techniques also go by the name of manipulation. Both exercises allow for the training of auxiliary or physiological motions.
What are the five passive stretches?
These passive stretches are the most flexible:
Running
Butterfly Sitting
Forward Fold Sitting
Sitting Straddling
References
- Patel, D. (2023a, September 3). Passive Range Of Motion Exercises – What it is?, How to do? Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/passive-range-of-motion-exercises/