Magnetotherapy
What is Magnetotherapy?
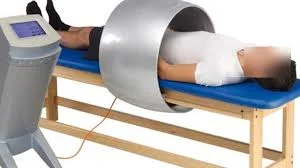
Magnetotherapy, also known as magnetic therapy, is a form of alternative medicine that involves the use of static magnetic fields to improve health and alleviate pain.
This treatment technique involves applying artificial magnetic fields to an affected human body area while adjusting the strength and frequency.
When we expose the damaged body’s region to a magnetic field similar to the Earth’s, we may acquire larger frequency and application duration with artificial magnetic fields.
Magnetotherapy is a physical treatment that involves applying particular magnetic fields to the human body. Magnetic fields play an important role in biological life; consider that the Earth itself is a massive magnet and that many living organisms adapt their lifestyles to the fluctuations in the Earth’s magnetism.
Magnetotherapy is used to treat pain, inflammation, and edema because it affects immune system cells and circulation. Furthermore, clinical investigations have demonstrated that magnetotherapy can effectively cure osteoporosis while also boosting fracture healing, soft tissue repair, and regeneration. It is utilized in orthopedics, sports medicine, physiotherapy, and other specialized fields. Given its therapeutic properties, it can be used alone or in conjunction with other therapies. To optimize both the application method and the treatment effects, several aspects must be considered.
- Selection of magnetic field and waveform.
- Application method: contact or targeted, broad or total.
- Various applicators.
Treatment modes include manual and automated. Equipment with various techniques for delivering a magnetic field to tissues.
What is the mechanism behind magnetotherapy:
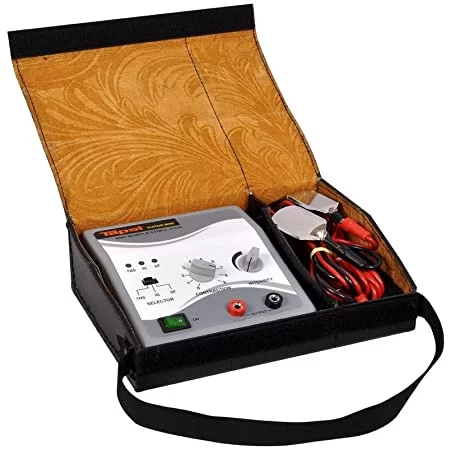
The magnetotherapy equipment employs electromagnetic radiation to carry out the therapy. The machine is made up of several magnets through which current flows and it generates an electromagnetic field with changing frequencies. There are two frequencies: low and high, which are employed depending on the difficulty. One of the most prevalent applications is to stimulate new tissue creation after a bone fracture.
The magnets are placed in touch with the patient’s body and create a magnetic field loaded with energy created by the machine’s computer. Magnets are attached to the body portions that require the greatest attention at the beginning of the therapy.
Magnets used in this therapy are generally rectangular plates with a Velcro attachment that allows them to be arranged in tiny bands around the treatment area. Some magnetotherapy equipment producers have also developed solutions that can be used while sleeping, such as a magnetized blanket that keeps the therapy going at night or a customized brace that covers the leg area.
The biological effects of magnetic fields:
- Cellular effects.
- Effects on Organs and Systems
Cellular effects.
Benefits of enriched oxygen in cells include improved oxygen utilization, increased metabolism, increased ATP generation, increased energy, and positive impacts on organs and systems.
- Osseous trophic effects
The magnetic field, due to the bone’s piezo-electric nature, improves the architectural course of osseous trabeculas in the damage zone, directing them in the same direction. This indicates that a better osseous callus is developed.
In conclusion, a specific number of exposures to a low-frequency magnetic field cause the production of a high-quality osseous callus in a short period.
- Magnetic fields:
Collagen production increases.
Calcium deposits grow and alter the osseous architectural process.
enhancement of hyaluronic acid production.
2. Vascular impact
Magnetic fields have been reported to enhance capillary neoformation, the development of pericytes in capillaries, and the opening of precapillary sphincters. , Local vasodilation occurs as a result of improved arterial circulation.
There is a rise in oxygen partial pressure.
3. Analgesic effects
There is a noticeable analgesic effect, although the cause is yet unclear.
Hypothesis: Increased synthesis of oligopeptides consisting of endorphins, encephalins, and encephalins, with effects at both the central and peripheral levels.
4. Autonomic nervous system impacts
Increased amounts of chemical mediators such as catecholamines or acetylcholine.
Depending on the direction of the nodular ganglion and vagus nerve in a field, an increase or inhibition of the nervous system
Transmission is seen. This is due to the magnetic field’s direction on the ions of the cellular membrane.
Types of artificial magnetic field:
Magnetic field treatment applies various magnets to the body to improve overall fitness. It may also be useful in treating some disorders.
There are several varieties, including:
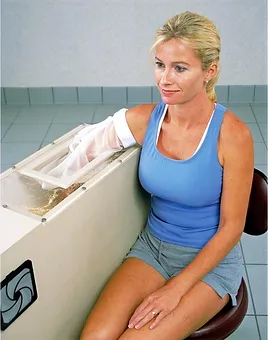
- Static magnetic field therapy: it involves touching a magnet to your skin. You may wear a magnetic bracelet or other magnetized jewelry. A magnet might be embedded in a bandage or used as a shoe insole. You might also sleep on a magnetic mattress pad.
- Electrically charged magnetic therapy (electromagnetic therapy): The magnets used here are electrically charged. Electromagnetic treatment is typically delivered by an electric pulse.
- Magnetic treatment and acupuncture: Magnets are applied to the same places of your skin that an acupuncturist would likely focus on during an acupuncture session; these areas are sometimes referred to as energy pathways or channels.
Indications of magnetotherapy:
Magnetic therapy is a non-invasive treatment for the musculoskeletal system. It works on the edema-contracture-pain triad, repairing and regenerating cutaneous, muscular, and bone tissues. Magnetic fields have a wide range of biological effects, including deep-seated tissues.
- Osteoporosis, fractures, and arthrosis
- Trauma, including contractures, sprains, strains, and fractures
- Pain, including tension headaches and neuralgia
- Skin lesions include burns, ulcers, and wounds.
- Inflammation, including arthritis, myositis, tendinitis, epicondylitis, lumbago, and adductor syndrome.
The therapeutic expectations can be concisely described as follows:
- Non-invasive and painless treatment
- Antalgic, anti-inflammatory, and draining effect
- Repairs tissues, even deep.
- spondylosis
- muscle spasm
- epicondylitis
- sciatica pain
- trigeminal neuralgia
- gout
- RA
- recent trauma
- fractures
- trophic ulcers
- CRPS
- Dupuytren’s contracture
- osteoporosis
- osteomyelitis acute and chronic
- dysmenorrhea and prostatitis
- sinusitis
- depression and migraines
Contraindications of magnetotherapy:
- Presence of acute illness- particularly septic TB.
- hemorrhagic foci (bleeding ulcers) might cause more hemorrhage due to the vasodilation effect.
- cardiac pacemakers.
- Pregnancy – because it might harm the fetus.
- tumors exist because they may spread.
- individuals undergoing hydrocortisone therapy.
- in the event of a vascular blockage, since the obstructive piece may be freed and impede another region of the body, causing more injury.
- juvenile diabetes – During PMF therapy, BGL should be evaluated.
What are the benefits of magnetotherapy:
Now that you understand the principle and significance of magnetotherapy, it’s time to learn about its primary advantages. Find out what they are below:
Encourages enhanced blood circulation.
In general, one of the most noticeable effects of magnetotherapy is improved blood circulation. This is because the magnetic field tends to diminish the contraction that blood vessels produce.
Provides immediate pain relief.
The magnetic field stimulates our bodies to manufacture endorphins, which are natural painkillers. In this way, it can be particularly useful for fractures, pain, and local discomfort.
Reduces inflammation.
This is purely due to increased circulation and a reduction in blood pH. As a result, the patient can get effective and speedy improvements in inflamed regions.
Enhanced cell regeneration.
Not just cells, but also bones and tissues. Magnetotherapy can improve cell function, and reduce and even prevent muscle and bone wear and tear, among other benefits.
Prevents aging.
Because magnetic treatment eliminates toxins that affect health and destroy cells, the procedure can help to prevent premature aging as well as the appearance of disorders associated with skin aging.
Application Rules:
The patient should not insert metal items into the solenoid since they can alter the magnetic field. Not to cause harm, but rather to modify magnetic field characteristics.
The therapy normally produces a speedy response, although this is dependent on the patient’s pathology, age, and other circumstances. If we find that the patient has moved along the curative process after ten sessions, we should discontinue the therapy since it indicates that the patient is not responding to the treatment.
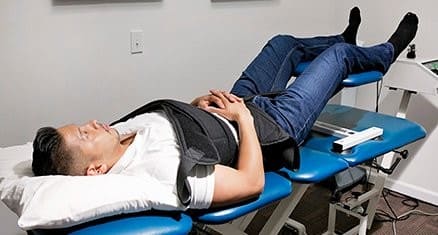
For optimal results, the patient’s affected zone should be in direct contact with the solenoid throughout therapy sessions lasting 30 minutes to 2 hours.
The sessions must be applied continually. If it is required to hasten the patient’s recovery, we might do two treatments on the same day with a 12-hour interval between them.
Electromagnetic field therapy can be used with other therapies.
BASIC GUIDELINES:
Begin treatments with lower settings and monitor responses to modify accordingly.
Pain may rise, which is a good sign that the patient is responding to the treatment.
BASIC RULES:
Pain intensity decreases at lower settings. If there is no change in the condition, move to a higher setting. Headaches and migraines should not be treated beyond 1-3mT, 2 Hz, 10 min. Patients with allergies may require lower settings. For patients with severe circulatory diseases, the recommended settings are 1-3 mT, 2-4 HZ, and 10- 20 minutes. Low settings may cause discomfort owing to increased blood flow in peripheral capillaries.
Side effects of magnetic field:
it may include;
- pain
- Nausea
- Dizziness
However, these adverse effects are uncommon.
Summary
Further research is needed to understand how magnetic fields affect biological systems, how treatment affects magnetic field parameters, and if distant therapeutic effects are possible. The methodology of previously conducted clinical trials should be thoroughly yet critically examined since the parameters stated in the study and the units in which they are expressed may create concerns.
The benefits of lengthier follow-up are especially noteworthy in research that employs disability questionnaires and quality-of-life assessments. Furthermore, the inclusion of a large and homogeneous group of patients in the study will provide clear evidence of the successful use of magnetotherapy in the treatment of patients with RA. This necessitates the thorough creation and dissemination of methodological standards for the use of magnetic fields to get the best possible results from such therapy.
FAQ’s
What exactly is magnetic treatment used for?
Magnets and magnetic treatment have been used for hundreds of years to cure a variety of pains, including arthritis and headaches. Magnetic treatment devices are readily available and are mostly utilized for pain relief, inflammatory disorders, and wound healing.
What is the mechanism behind magnetotherapy?
Perhaps the most often proposed explanation is that magnets enhance blood flow in underlying tissues.
What are the advantages of magnetic cupping?
It assists in lifting and stretching soft tissue to separate fascia and limitations. It can also assist in improving joint mobility and flexibility. Cupping promotes good circulation and opens up the energy flow in the body.
What are the downsides of magnetic therapy?
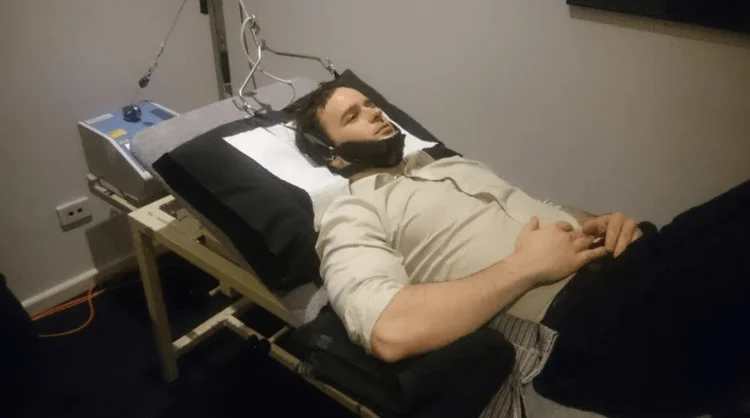
Side effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation:
Mild headaches are most prevalent.
lightheadedness.
Scalp pain.
Neck discomfort.
tingling.
Facial twitches.
sleepiness.
changed cognition during the therapy.
What is the indication for magnetotherapy?
Magnetotherapy in physiotherapy is used to treat bone and joint disorders, osteoporosis, skin ailments, and female health difficulties.
What are the fundamentals of magneto therapy?
The fundamental premise of pulsed magnetic (PEMF) treatment is the creation of electromagnetic pulses. These pulses penetrate the garments as well as the whole depth of the tissue to reach the desired application spot.
Can magnets decrease swelling?
Magnets have been shown in studies to greatly decrease edema when administered soon after tissue damage.
Can magnets relieve back pain?
Magnets have been recommended as a pain reliever, particularly for low back and knee discomfort. Magnets can be worn as bracelets, taped to your joints, or utilized in a variety of magnetic devices, such as mattress pads.
Can magnets influence your body?
A powerful magnetic field is not harmful to the human body if handled carefully.
What are the limitations of magnetotherapy?
Magnetotherapy has some limitations, including potential side effects such as dizziness, low energy, palpitation, nausea, and vomiting, as well as a decrease in blood pressure or itchy, burning, and painful skin areas. However, these side effects are rare.
Do magnets affect nerves?
Magnets have no detrimental or beneficial effects on the brain, nerves, blood, or any other component of the body.
References
- Magnetotherapy: what it is, what it is used for, and ideal devices – Sixtus Italia. (n.d.-b). Sixtus Italia. https://www.sixtusitalia.com/electromedical/magnetotherapy/
- Barduzzi, G. (2022, August 26). Discover The Benefits of Magnetotherapy. GB Sports Physio. https://www.gbsportsphysio.com/post/discover-the-benefits-of-magnetotherapy
- Dhameliya, N. (2023b, January 2). MAGNETOTHERAPY USE IN PHYSIOTHERAPY. Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic. https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/magnetotherapy-use-in-physiotherapy/
- Ellis, R. R. (2023, June 3). What Is Magnetic Field Therapy? WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/magnetic-field-therapy-overview