Back Stiffness
Introduction
Back stiffness is most often caused by lumbar strains (strains of the muscles or ligaments) or lumbar arthritis. The first episode of the symptoms is the strongest indicator of stiffness in the lumbar spine. Over the years, those with lumbar spine arthritis who have stiffness typically see increased symptoms. Conversely, muscular stiffness is generally associated with acute trauma, where the back muscles stiffen up and become immobile (e.g., lifting a big weight improperly). Both are frequent situations that are partly caused by growing obesity rates and aging.
The feelings of stiffness brought on by lumbar spine arthritis often worsen over the years. Conversely, a strain is typically associated with acute trauma (e.g., wrong lifting of a large weight). The back muscles tighten and freeze up as a result.
Causes of Back Stiffness
Ankylosing Spondylitis: A condition known as ankylosing spondylitis inhibits the fusion of vertebrae by inflaming the spine. Pain and stiffness in the lower back are symptoms of the illness. Stiffness normally goes away with activity but not with rest.
Bad Posture: Sitting for extended periods damages the discs in your spine, weakens the muscles in your upper and lower back, and stops the spinal tissue from receiving nutrition. To reduce back pain and stiff lower back pain from extended sitting, sit with good posture and do easy stretches and exercises to keep your muscles working. Use an office chair’s backrest sparingly. Sit up straight when doing core exercises.
Muscle or ligament strain:
Frequent heavy lifting or an abrupt uncomfortable movement might cause strain on your back muscles and spinal ligaments. Constant tension on your back might cause severe muscle spasms if you are not in good physical health.
Arthritis:
The cartilage in our joints, which acts as a lubricant and shock absorber where the bones connect and move against one another, is damaged by osteoarthritis. Additionally, it can be present between the vertebrae, which are the bones that comprise your spine.
Your lower back becomes inflamed and stiff as a result of the vertebrae’s inability to glide smoothly against one another due to the drying and shrinking of the spine’s cartilage.
Other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, can also harm joints, including your spine, but they are less frequent.
Occasionally, back pain and tightness may be caused by an underlying condition. Among the possible reasons are:
- infections
- tumors
- Cauda equina syndrome
- An uncommon and dangerous consequence of a ruptured disc.
Symptoms of Back Stiffness
Back tightness can be accompanied by back pain, cramps, and spasms. The back may feel stiff, tight, and cramped, and the pain frequently seems like a dull, continuous aching. Additionally, stiffness in the legs, hips, and pelvis may also occur.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Suppose you’ve had a tight lower back for longer than two weeks. You can’t do everyday duties because of your back pain. In the morning, I have terrible back stiffness. Your symptoms have gotten worse after you were diagnosed with arthritis or another disease. Go to urgent treatment if your pain appears very acute or disruptive. If you have any of the following symptoms, you should go to a hospital or urgent care facility immediately:
- Back pain and fever
- Back pain following a vehicle accident, fall, or other traumatic event
- A lack of bladder or bowel control
- loss of limb strength, tingling, or numbness
- Back pain and unexplained weight loss
Back Stiffness Treatment
The American College of Physicians advises beginning non-pharmacological therapy for low back pain.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy
- Low-level laser therapy
- Reducing stress using meditation and other methods.
Medicines:
Advil (ibuprofen) and Aleve (naproxen), two over-the-counter analgesics, can help reduce back pain and stiffness. If over-the-counter medications aren’t working, your doctor may occasionally recommend prescription NSAIDs like Celebrex (celecoxib) and muscle relaxants.
PHYSICAL THERAPY TREATMENT
Back stiffness can be treated with physical therapy. Facilitating everyday tasks and activities is the main goal of physical therapy. Reducing back pain and increasing flexibility are the two main objectives of manual therapy. This will lessen soft tissue pain, improve circulation, and relax muscles.
To increase flexibility, soft movements, and mobilization methods will be used to push, pull, or twist bones and joints into place. As therapy continues, exercises back stretches, and lifestyle advice will be given to assist reduce lower back stiffness.
Exercises
Stiffness in the lower back can be relieved with mild back exercises and stretches.
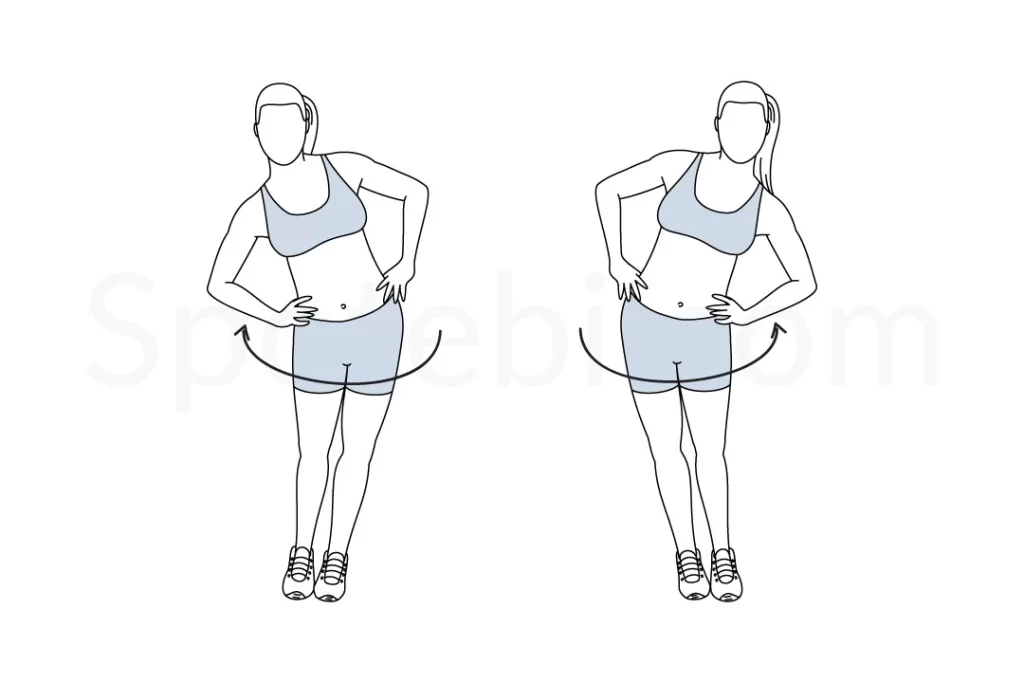
Hip circles:
Stand with feet slightly wider than hip-width apart. Make a round, hula-hooping motion with your hands on your hips. As you move gently, observe when you feel the most stiff. You should gradually extend your hips in the direction of any restricted areas you identify.
Lower back rotation:
You should lie straight with your knees bent and bases supported on the ground. Your shoulders should stay flat on the floor while you progressively shift your knees to one side. Switch legs after ten seconds of holding.

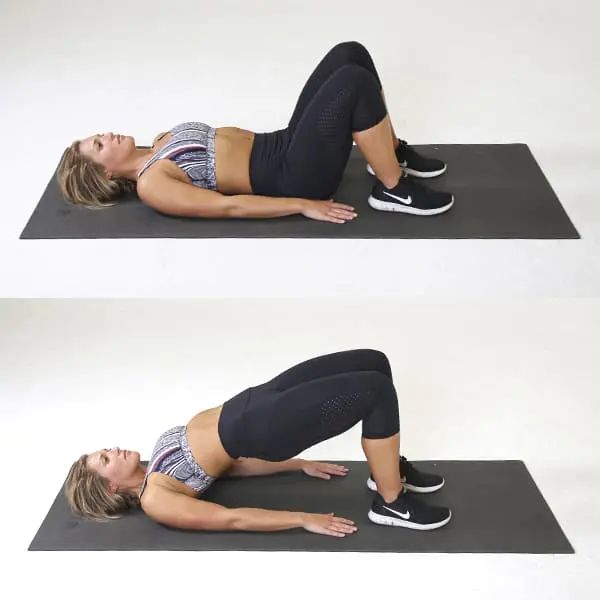
Pelvic Bridging: Patient should lie straight with both hands supported on the ground and knees bent. Patient should elevate their hips will applying downward force with their shoulders. After five seconds of holding, let go and do it again.

Self-care for a stiff back
Heat: Heat helps relax muscles and lessen joint pain by increasing blood flow. Heat can help relieve the pain of arthritis or injuries older than six weeks.
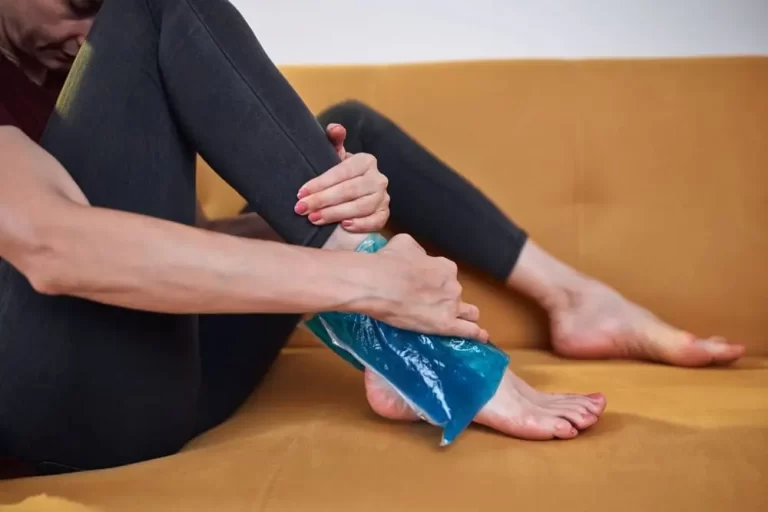
Ice: By narrowing blood vessels, ice can reduce inflammation and decrease pain.
Activity: Perform slight exercise, like yoga, to remain moving because bed rest may worsen stiffness. Stay cautious of tasks that require heavy lifting or back twisting.
Prevention
However, back pain and stiffness are common issues, and the following could still decrease the risk:
- Avoid smoking, since this might alter blood flow and raise the chance of injury.
- Regularly exercising
- Wearing comfortable, supportive footwear.
- Using lumbar supports to maintain proper posture, eating a balanced diet, reaching or maintaining an appropriate weight, avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity, and lifting heavy things with the knees without additionally twisting the lower back.
Summary
The most common causes of back pain are acute injuries from activities that strain the back muscles or lumbar spine arthritis. Poor posture can also cause back stiffness. Simple therapies like stretching and applying heat and cold can usually help and improve posture helps to reduce back stiffness.
FAQ’s
Why is my back constantly stiff?
A strained muscle or lumbar spine arthritis is the most common cause of a stiff back.
What disease causes back stiffness?
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Stiffness may result from inflammation in the spine’s joints and tissues if you have ankylosing spondylitis.
How do I loosen my tight back?
Heat or ice therapy are two natural treatments that may help ease lower back pain.
massage therapy.
self-massage using a foam roller at home.
physical therapy
yoga
spinal manipulation
and acupuncture.
References:
- Frothingham, S. (2018, October 17). Why do I have a stiff back and what can I do about it? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/stiff-back#causes
- Cluett, J., MD. (2024b, August 30). Stiff Back Causes and Treatment. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/back-pain-symptoms-stiffness-2549270
- Adela. (2024c, June 19). Back Stiffness. Orchard Health Clinic – Osteopathy, Physiotherapy and Chiropractic. https://www.orchardhealthclinic.com/tight-back-muscles
- Stiff Back | Causes, Exercises, Prevention, and Treatments. (n.d.-c). https://www.mypremierpain.com/blog/back-pain/stiff-back-causes-and-treatment



back stiff cant hard walk help